Designing Yoga Therapy Sessions

In this extract from our Yoga Therapy Greece first year training manual we discuss what is yoga therapy, how does yoga differ from yoga and what does a yoga therapy session consist of. We of course throughout our training go into all these elements in a lot greater depth, detail, with theory, practice and a lot of personal guidance and support.
Yoga differs from religion in that unlike religions, belief in God is optional and in religion God is the goal, while in Yoga, faith to any particular God is merely a tool to achieve the true goals of Yoga, a stable mind, freedom and more sustained joy.
According to Patanjali, for Yoga to be safe and effective, it must always be adapted to the needs, goals and limitations of each practitioner. Desikachar also cites Sutra 3.6 which emphasises ‘viniyoga’ the need for individualization.
Desikachar in the 1970’s has noticed that most Yoga teachers were teaching the same or similar practice to every student, irrespective of the student’s age, abilities or interests, so he shared the art of viniyoga.
Viniyoga is the yoga that addresses the personal needs of the individuals either strengthening the body or the mind (Shakti), their spiritual evolution (Adhyātmika), either for prevention (Raksana) or for therapeutic reasons (Cikitsa). Whatever the reason, the need for personal sadhana is crucial. So viniyoga can be considered the mother of yoga therapy.
Benefits from the personal and sophisticated approach of Yoga
- It makes Yoga non-exclusive, personal and universal
- Respect for the uniqueness of each individual
- It makes possible to have a safe practice for everyone
- Helps us accept limitations and cultivate more patience
- Reduces risk of injury as a preventive intervention
- Can truly help with many chronic illnesses
- Compliments other health care systems
- Often works when more conventional approaches cannot
- Helps us deal with life’s inevitable changes
Yoga Therapy according to IAYT (International Association of Yoga Therapists)is the professional application of the principles and practices of yoga to promote health and well-being within a therapeutic relationship that includes personalized assessment, goal setting, lifestyle management, and yoga practices for individuals or small groups. It is not something new. It is based on traditional practices and ancient teachings such as.
1. SVADAYA. Recognizing the needs & the habits (samskaras).
2. SANKALPA. Come up with clear goal (s)
3. TAPAS. Have the discipline to practice that which supports the change
4. ISVARA PRANIDHANA. Faith in a bigger power
The goals of Yoga Therapy are to eliminate/reduce/manage the symptoms of suffering, improve function and movement, prevent recurrence by changing dysfunctional breathing and movement, habits and thinking patterns, enhance self-acceptance and self-compassion and motivate the individual to commit to a self-care practice that will facilitate a desired change or acceptance.
More specifically the goals can be to reduce pain, to increase range of motion, to find a resting position, to enhance sleep, to calm the mind, to enhance breathing capacity, to reduce inflammation, to empower, to enhance faith, to facilitate the change, to see what really matters, to increase awareness/mindfulness, to establish a better relationship within themselves and with others.
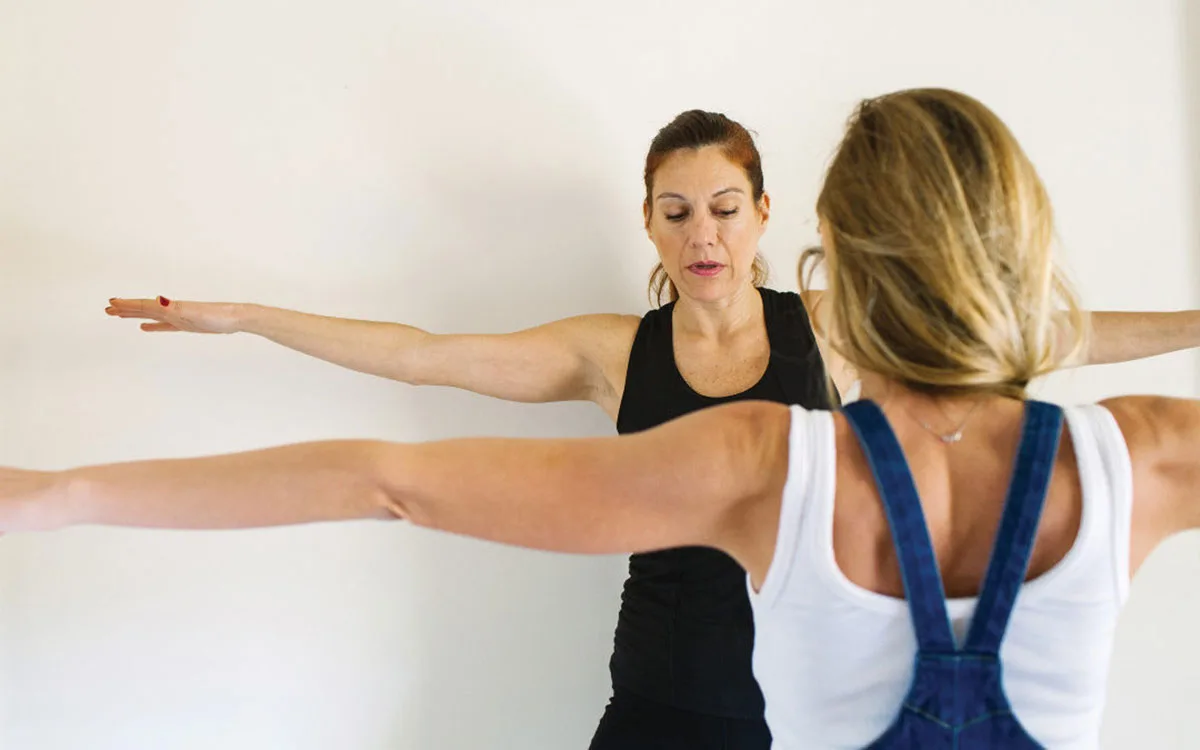
The orientations of a Yoga Therapist are to understand the person’s emotional response and how they feel regarding the condition(s), to identify dysfunctional patterns that dissipate energy, help them balance their energy and motivate them to change and move towards their sankalpa and their full realization.
The biggest difference between Yoga and Yoga Therapy is that in Yoga we focus on the asana and how to do it, while in Yoga Therapy we focus on the person and we use all the yoga tools besides the asanas to change misalignments/ habits/samskaras and find relief. The non-functional patterns-samskaras may be relating to the body, breath and mind. We have access to them with asanas, pranayama, mantras, relaxation respectively, after we connect.
So, ‘Yoga Therapy’ is based on the following principles:
- Respect the ability and limitations of the student
- Link all movement with breathing
- Only practice that which makes the breath slow and deep
- Teach what is only appropriate to the student
- Move in and out of poses before holding (repetitions before stay)
- Sequence practices intelligently (vinyasa karma) to avoid any discomfort or injury
- Use supports, props (chairs, walls etc) to accommodate individual needs
- Offer supervision
- Continue to modify tools as conditions change
- Rest between poses and when needed
- Teach 1-2-1 and special group classes)
- Suggest lifestyle changes
- Respect medical advice
Yoga Therapy starts with the Yoga Therapist belief: I AM HERE FOR YOU
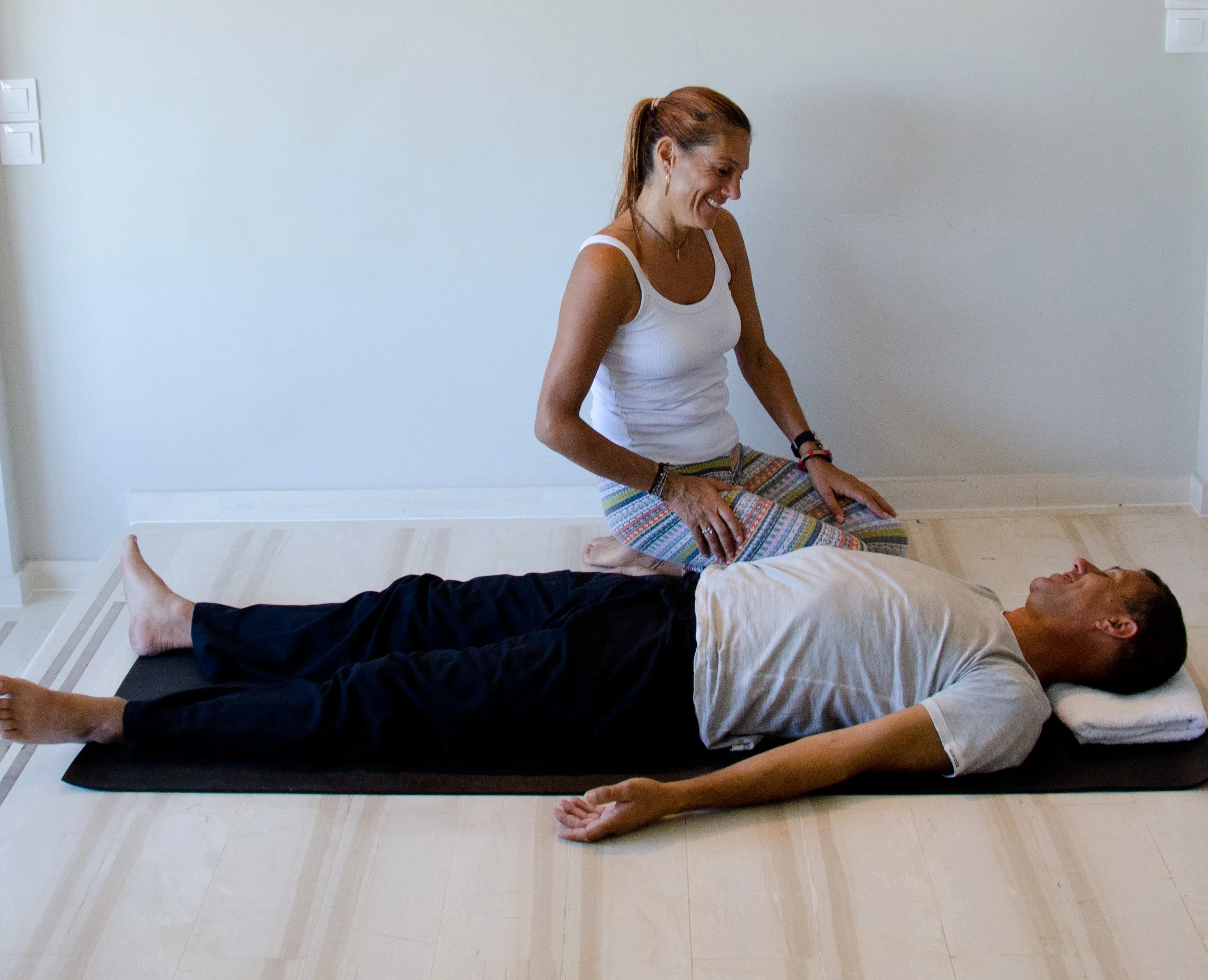
The Yoga Therapy session of 90 minutes consist of:
A. Interview for 20-30 minutes
B. Postural, Movement and Breathing Assessment for 20-30 minutes (in the 1st session)
C. Relaxation/Breathing in a restorative posture for 5 minutes
D. Practice for 30-40 minutes. Try, design, explain and draw a practice sheet
(E. Keep a record)